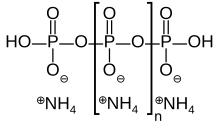
Ammonium polyphosphate
Its chemical formula is H(NH4PO3)nOH showing that each monomer consists of an orthophosphate radical of a phosphorus atom with three oxygens and one negative charge neutralized by an ammonium cation leaving two bonds free to polymerize.
However, iron and aluminum impurities, soluble in concentrated phosphoric acid, form gelatinous precipitates or "sludges" in ammonium polyphosphate at pH between 5 and 7.
[4] However, depending on the degree of polymerization, ammonium polyphosphate can act as a chelating agent to keep certain metal ions dissolved in solution.
In the gas phase, the release of non-flammable carbon dioxide helps to dilute the oxygen of the air and flammable decomposition products of the material that is burning.
In the condensed phase, the resultant carbonaceous char helps to shield the underlying polymer from attack by oxygen and radiant heat.