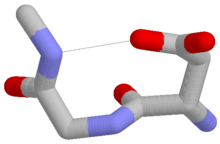
Asx turn
The Asx turn[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] is a structural feature in proteins and polypeptides.
The name "Asx" is used here to represent either of the amino acids aspartate (Asp) or asparagine (Asn).
Asx and ST turns both occur frequently at the N-termini of α-helices.
Similar motifs occur with serine or threonine as residue i, which are called ST turns.
[13] In spite of serine and threonine having one less sidechain atom, such that the sidechain-mainchain mimicry of β turns is imperfect, these features occur in proteins as the four types in numbers approaching those of Asx turns.