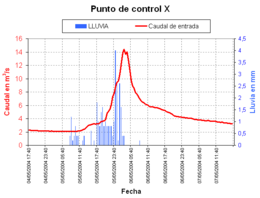
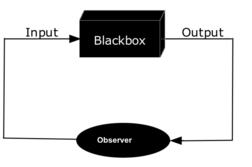
Black box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings.
In systems theory, the black box is an abstraction representing a class of concrete open system which can be viewed solely in terms of its stimuli inputs and output reactions: The constitution and structure of the box are altogether irrelevant to the approach under consideration, which is purely external or phenomenological.
In other words, only the behavior of the system will be accounted for.The understanding of a black box is based on the "explanatory principle", the hypothesis of a causal relation between the input and the output.
[14] In humanities disciplines such as philosophy of mind and behaviorism, one of the uses of black box theory is to describe and understand psychological factors in fields such as marketing when applied to an analysis of consumer behaviour.
[15][16][17] Black Box theory is even wider in application than professional studies: The child who tries to open a door has to manipulate the handle (the input) so as to produce the desired movement at the latch (the output); and he has to learn how to control the one by the other without being able to see the internal mechanism that links them.
In our daily lives we are confronted at every turn with systems whose internal mechanisms are not fully open to inspection, and which must be treated by the methods appropriate to the Black Box.(...)
This simple rule proved very effective and is an illustration of how the Black Box principle in cybernetics can be used to control situations that, if gone into deeply, may seem very complex.