Carbonium ion
In chemistry, a carbonium ion is a cation that has a pentacoordinated carbon atom.
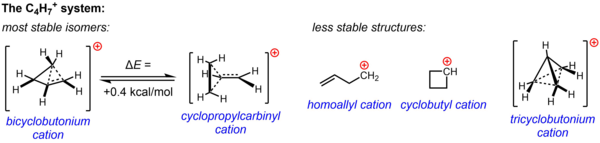
A non-classical structure for C4H+7 is supported by substantial experimental evidence from solvolysis experiments and NMR studies.
[4] The low temperature NMR spectrum of a dimethyl derivative shows two methyl signals, indicating that the molecular conformation of this cation is not perpendicular (as in A), which possesses a mirror plane, but is bisected (as in B) with the empty p-orbital parallel to the cyclopropyl ring system: In terms of bent bond theory, this preference is explained by assuming favorable orbital overlap between the filled cyclopropane bent bonds and the empty p-orbital.
In these ions, a single carbon atom hovers over a four- or five-sided polygon, in effect forming a pyramid.
[12] Carbonium ions are intermediates in the isomerization of alkanes catalyzed by very strong solid acids.