Catalyst support
For example, an acidic solution of aluminium salts and precatalyst are treated with base to precipitate the mixed hydroxide, which is subsequently calcined.
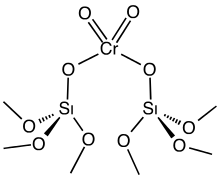
The Phillips catalyst, consisting of chromium oxide supported on silica, is activated by a stream of hot air.
[5] A common problem in heterogeneous catalysis is leaching, a form of deactivation where active species on the surface of a solid catalyst are lost in the liquid phase.
[7] Strong metal-support interaction is another case highlighting the oversimplification that heterogeneous catalysts are merely supported on an inert substance.
However, the technique has not proven commercially viable, usually because the heterogenized transition metal complexes are leached from, or deactivated by, the support.
Supports immobilize the particle reducing its mobility and favouring the chemical stabilization: they can be considered as solid capping agents.
[10] One of the most promising supports is graphene for its porosity, electronic properties, thermal stability and active surface area.