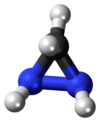
Diaziridine
Diaziridines are heterocyclic compounds containing two nitrogen atoms in a three-membered ring.
Unlike most amine types of structures, the nitrogen atoms of diaziridines are configurationally stable because the ring strain prevents Walden inversion.
As a result, there can be various stereoisomeric forms of this structure.
They are usually synthesized by treating a carbonyl compound with an aminating reagent like hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid and either ammonia or a primary aliphatic amine under slightly basic conditions.
[1] The final step is based on the intramolecular cyclization of an aminal.