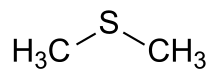
Dimethyl sulfide
It is a component of the smell produced from cooking of certain vegetables (notably maize, cabbage, and beetroot) and seafoods.
DMS is also produced naturally by bacterial transformation of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) waste that is disposed of into sewers, where it can cause environmental odor problems.
[9] Among these compounds, sulfuric acid has the potential to create new aerosols which act as cloud condensation nuclei.
Through this interaction with cloud formation, the massive production of atmospheric DMS over the oceans may have a significant impact on the Earth's climate.
Those compounds are components of an odor like rotting meat, which attracts various pollinators that feed on carrion, such as many species of flies.
[17] On September 12, 2023, NASA announced that their investigation into exoplanet K2-18b revealed the possible presence of dimethyl sulfide, noting "On Earth, this is only produced by life.
Some reports claim that DMS has a low olfactory threshold that varies from 0.02 to 0.1 ppm[clarification needed] between different persons, but it has been suggested that the odor attributed to dimethyl sulfide may in fact be due to disulfides, polysulfides and thiol impurities, since the odor of dimethyl sulfide is much less disagreeable after it is freshly washed with saturated aqueous mercuric chloride.
In the Victorian era, before DMS was discovered, the origin of sea air's 'bracing' aroma was attributed to ozone.
[28] Dimethyl sulfide is the main volatile chemical produced by various species of truffle, and is the compound that animals trained to uncover the fungus (such as pigs and detection dogs) sniff out when searching for them.