Field effect (chemistry)
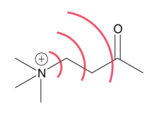
[1] This field, which is substituent and conformation dependent, can influence structure and reactivity by manipulating the location of electron density in bonds and/or the overall molecule.
[3] Field effects are relatively weak, and diminish rapidly with distance, but have still been found to alter molecular properties such as acidity.
[1] The directionality of a dipole, and concentration of charge, can both define the shape of a molecule's electric field which will manipulate the localization of electron density toward or away from sites of interest, such as an acidic hydrogen.
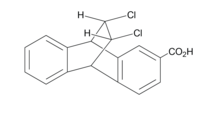
[4] The C-X dipole is oriented away from the carboxylic acid group, and can draw electron density away because the molecule center is empty, with a low dielectric constant, so the electric field is able to propagate with minimal resistance.
[8] These effects can therefore help to tune the acidity/basicity of a molecule to protonate/deprotonate a specific compound, or enhance hydrogen bond-donor ability for molecular recognition or anion sensing applications.
[16] When the chlorines are pointed over the carboxylic acid group, the pKa is higher because loss of a proton is less favorable due to the increase in negative charge in the area.