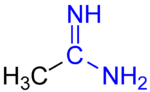
Amidine
The resulting cationic species is known as an amidinium ion[8] and possesses identical C-N bond lengths.
Examples include the antiprotozoal imidocarb, the insecticide amitraz, xylamidine, an antagonist at the 5HT2A receptor,[9] and the anthelmintics amidantel and tribendimidine.
Formamidinium (see below) may be reacted with a metal halide to form the light-absorbing semiconducting material in perovskite solar cells.
[10][11][12] When the parent oxoacid is a carboxylic acid, the resulting amidine is a carboxamidine or carboximidamide (IUPAC name).
[13][14] An amidinate salt has the general structure M+[RNRCNR]− and can be accessed by reaction of a carbodiimide with an organometallic compound such as methyl lithium.