Formate
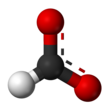
Formate (IUPAC name: methanoate) is the conjugate base of formic acid.
The two oxygen atoms are equivalent and bear a partial negative charge.
Formate (or formic acid) is invoked as a leaving group in the demethylation of some sterols.
Specific conversions include testosterone to estradiol and androstenedione to estrone.
Methanol and carbon monoxide react in the presence of a strong base, such as sodium methoxide:[1] Hydrolysis of methyl formate gives formic acid and regenerates methanol: Formic acid is used for many applications in industry.