Geography of India
India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands, some 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) southeast of the mainland, share maritime borders with Myanmar, Thailand and Indonesia.
[6] India's territorial waters extend into the sea to a distance of 12 nautical miles (13.8 mi; 22.2 km) from the coast baseline.
The northern frontiers of India are defined largely by the Himalayan mountain range, where the country borders China, Bhutan, and Nepal.
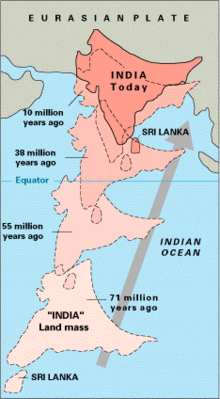
About 90 million years ago, during the late Cretaceous Period, the Indian Plate began moving north at about 15 cm/year (6 in/yr).
[9] The collision with the Eurasian Plate along the modern border between India and Nepal formed the orogenic belt that created the Tibetan Plateau and the Himalayas.
Its western border with Pakistan extends up to 3,323 km (2,065 mi), dividing the Punjab region and running along the boundaries of the Thar Desert and the Rann of Kutch.
[1] This border runs along the Indian states and union territories of Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
[11] Both nations delineated a Line of Control (LoC) to serve as the informal boundary between the Indian and Pakistan-administered areas of the Kashmir region.
[19] The Siliguri Corridor, narrowed sharply by the borders of Bhutan, Nepal and Bangladesh, connects peninsular India with the northeastern states.
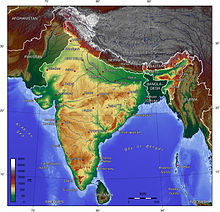
They are: An arc of mountains consisting of the Himalayas, Hindu Kush, and Patkai ranges define the northern frontiers of the Indian subcontinent.
[citation needed] The Himalayas in India extend from Ladakh in the north to the state of Arunachal Pradesh in the east.
[citation needed] This is a large region of the Indian subcontinent located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada River.Having once constituted a segment of the ancient continent of Gondwanaland, this land is the oldest and most stable in India.
[31] One such passage is the Bhor Ghat that connects the towns Khopoli and Khandala, on NH 4 about 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of Mumbai.
They run parallel to the Himalayas, from Jammu and Kashmir in the west to Assam in the east, drain most of northern and eastern India and extend into Pakistan.
The great plains are sometimes classified into four divisions: The Indo-Gangetic belt is the world's most extensive expanse of uninterrupted alluvium formed by the deposition of silt by the numerous rivers.
The Kutch city of Bhuj was the epicentre of the 2001 Gujarat earthquake, which claimed the lives of more than 1,337 people and injured 166,836 while destroying or damaging near a million homes.
[54] They consist of 572 islands, lying in the Bay of Bengal near the Myanmar coast running in a north–south axis for approximately 910 km.
[56] Temperature rises on the Tibetan Plateau are causing Himalayan glaciers to retreat, threatening the flow rate of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Indus, Yamuna and other major rivers.
A 2007 World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) report states that the Indus River may run dry for the same reason.
[59] According to some current projections, the number and severity of droughts in India will have markedly increased by the end of the present century.
[64] The heavy southwest monsoon rains cause the Brahmaputra and other rivers to distend their banks, often flooding surrounding areas.
[68] Mangrove forests are present all along the Indian coastline in sheltered estuaries, creeks, backwaters, salt marshes and mudflats.
The Sundarbans are intersected by a complex network of tidal waterways, mudflats and small islands of salt-tolerant mangrove forests.
The area is known for its diverse fauna, being home to a large variety of species of birds, spotted deer, crocodiles and snakes.
[82] Most of India's estimated 5.4 billion barrels (860,000,000 m3) in oil reserves are located in the Mumbai High, upper Assam, Cambay, the Krishna-Godavari and Cauvery basins.
[76] India possesses about seventeen trillion cubic feet of natural gas in Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat and Odisha.
)[83] Based on the Köppen system, India hosts six major climatic subtypes, ranging from arid desert in the west, alpine tundra and glaciers in the north, and humid tropical regions supporting rainforests in the southwest and the island territories.
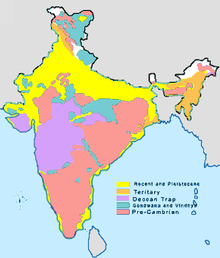
[88] The Paleozoic formations from the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian and Devonian system are found in the Western Himalaya region in Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh.
[90] It is derived from the deposition of silt carried by rivers and are found in the Great Northern plains from Punjab to the Assam valley.
A shield is the part of a craton where basement rock crops out of the ground, and it is relatively the older and more stable section, unaffected by plate tectonics.