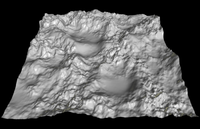
Heightmap
In computer graphics, a heightmap or heightfield is a raster image used mainly as Discrete Global Grid in secondary elevation modeling.
When the map is rendered, the designer can specify the amount of displacement for each unit of the height channel, which corresponds to the “contrast” of the image.
Heightmaps are commonly used in geographic information systems, where they are called digital elevation models.
Heightmaps are an ideal way to store digital terrain elevations; compared to a regular polygonal mesh, they require substantially less memory for a given level of detail.
Most modern 3D computer modelling programs are capable of using data from heightmaps in the form of bump, normal, or displacement maps to quickly and precisely create complex terrain and other surfaces.