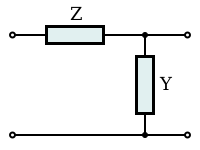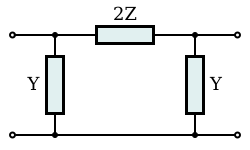Image impedance
Zi 2 is found by a similar process, but it is simpler to work in terms of the reciprocal, that is image admittance Yi 2, Also, it can be seen from these expressions that the two image impedances are related to each other by: Directly measuring image impedance by adjusting terminations is inconveniently iterative and requires precision adjustable components to effect the termination.
The image impedance is then given by, This method requires no prior knowledge of the topology of the network being measured.
In fact, in the limiting case of a chain of cascaded networks where the size of each single network is approaching an infinitesimally small element, the mathematical limit of the image impedance expression is the characteristic impedance of the chain.
Conversely, it is possible to analyse a transmission line with lumped components, such as one utilising loading coils, in terms of an image impedance filter.
term represents the voltage ratio that would be observed if the maximum available power was transferred from the source to the load.
In the case of a network with symmetrical image impedances, such as a chain of an even number of identical L sections, the expression reduces to, In general, γ is a complex number such that, The real part of γ, represents an attenuation parameter, α in nepers and the imaginary part represents a phase change parameter, β in radians.
For a reciprocal network (AD−BC=1), the image impedances can be expressed[4] in terms of ABCD parameters as, The image propagation term, γ may be expressed as, Note that the image propagation term for a transmission line segment is equivalent to the Propagation constant of the transmission line times the length.