Interglacial
During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets.
Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a specific age are used to identify particular interglacials.
Commonly used are mammalian and molluscan species, pollen and plant macro-remains (seeds and fruits).
[2] Interglacials are a useful tool for geological mapping and for anthropologists, as they can be used as a dating method for hominid fossils.
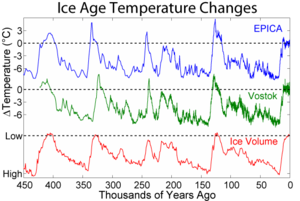
The oxygen isotope ratio obtained from seabed sediment core samples, a proxy for the average global temperature, is an important source of information for changes in Earth's climate.
The last six interglacials are: Hypothetical runaway greenhouse state Tropical temperatures may reach poles Global climate during an ice age Earth's surface entirely or nearly frozen over