Inverted yield curve
[4][5][6][7] The term "inverted yield curve" was coined by the Canadian economist Campbell Harvey in his 1986 PhD thesis at the University of Chicago.
In this view, an inverted yield curve implies that investors expect lower interest rates at some point in the future – for example, when the economy is expected to enter a recession and the Federal Reserve reduces interest rates to stimulate the economy and pull it out of recession.
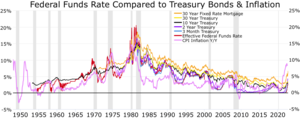
[12][13] It has often been said that the inverted yield curve has been one of the most reliable leading indicators for economic recession during the post–World War II era.
[19] The longest and deepest Treasury yield curve inversion in history began in July 2022, as the Federal Reserve sharply increased the fed funds rate to combat the 2021–2023 inflation surge.
An earlier survey of bond market strategists found a majority no longer believed an inverted curve to be a reliable recession predictor.










Inverted yield curve in the first half of 2022 during Sri Lankan economic crisis



Inverted yield curve in 1990
Zero interest-rate policy starting in 1999 [ 24 ]
Negative interest rate policy started in 2014

Inverted yield curve in 1994–1998 and 2004–2008