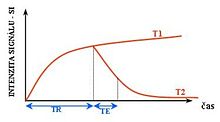
MRI pulse sequence
To create a T1-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to recover before measuring the MR signal by changing the repetition time (TR).
To create a T2-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to decay before measuring the MR signal by changing the echo time (TE).
This image weighting is useful for detecting edema and inflammation, revealing white matter lesions, and assessing zonal anatomy in the prostate and uterus.
[citation needed] Inversion recovery is an MRI sequence that provides high contrast between tissue and lesion.
[41] Clinically, diffusion MRI is useful for the diagnoses of conditions (e.g., stroke) or neurological disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis), and helps better understand the connectivity of white matter axons in the central nervous system.
The DWI enhancement appears within 5–10 minutes of the onset of stroke symptoms (as compared to computed tomography, which often does not detect changes of acute infarct for up to 4–6 hours) and remains for up to two weeks.
Perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) is performed by 3 main techniques: The acquired data is then postprocessed to obtain perfusion maps with different parameters, such as BV (blood volume), BF (blood flow), MTT (mean transit time) and TTP (time to peak).
[48][49] Researchers use statistical methods to construct a 3-D parametric map of the brain indicating the regions of the cortex that demonstrate a significant change in activity in response to the task.
The CBV method requires injection of a class of MRI contrast agents that are now in human clinical trials.
Because this method has been shown to be far more sensitive than the BOLD technique in preclinical studies, it may potentially expand the role of fMRI in clinical applications.
The CBF method provides more quantitative information than the BOLD signal, albeit at a significant loss of detection sensitivity.
[citation needed] Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based to image blood vessels.
This method exploits the susceptibility differences between tissues and uses a fully velocity-compensated, three-dimensional, RF-spoiled, high-resolution, 3D-gradient echo scan.
Implementation of homonuclear magnetization transfer involves choosing suitable frequency offsets and pulse shapes to saturate the bound spins sufficiently strongly, within the safety limits of specific absorption rate for MRI.
[58] Techniques to suppress fat on MRI mainly include:[59] This method exploits the paramagnetic properties of neuromelanin and can be used to visualize the substantia nigra and the locus coeruleus.
At the slowest extreme the interaction time is effectively infinite and occurs where there are large, stationary field disturbances (e.g., a metallic implant).
T2 is a measure of the loss of coherence that excludes static dephasing, using an RF pulse to reverse the slowest types of dipolar interaction.
In general, the rate of decay of an ensemble of spins is a function of the interaction times and also the power of the RF pulse.