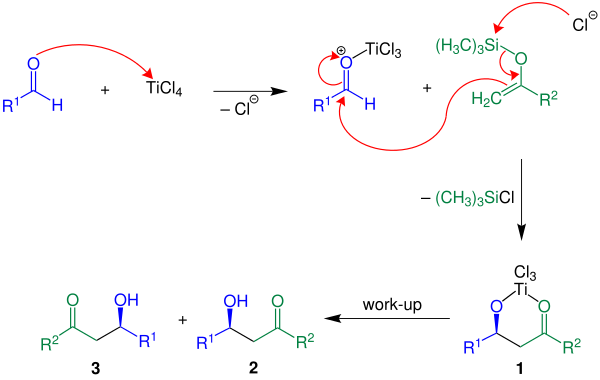
Mukaiyama aldol addition
Whether the anti-diastereomer or the syn-diastereomer is built depends largely on reaction conditions, substrates and Lewis acids.
At room temperature it produces a diastereomeric mixture of threo (63%) and erythro (19%) β-hydroxyketone as well as 6% of the exocyclic, enone condensation product.
In its original scope the Lewis acid (titanium tetrachloride, TiCl4) was used in stoichiometric amounts but truly catalytic systems exist as well.
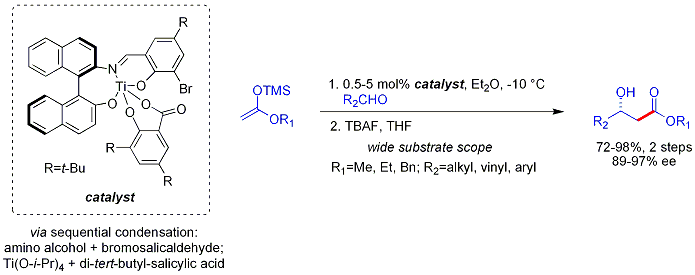
Carreira has described particularly useful asymmetric methodology with silyl ketene acetals, noteworthy for its high levels of enantioselectivity and wide substrate scope.
The example shown below works efficiently for aromatic (but not aliphatic) aldehydes and the mechanism is believed to involve a chiral, metal-bound dienolate.
[10] Mukaiyama employed in his rendition of taxol total synthesis (1999) two aldol additions,[11][12] one with a ketene silyl acetal and excess magnesium bromide: and a second one with an amine chiral ligand and a triflate salt catalyst: Utilization of chiral Lewis acid complexes and Lewis bases in asymmetric catalytic processes is the fastest-growing area in the usage of the Mukaiyama aldol reaction.