Olivetol
[2][3] The cannabis plant produces the related substance olivetolic acid (OLA), which may be involved in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
[6] In PiHKAL, Alexander Shulgin reports a cruder method of producing the same product by bringing to reaction olivetol and the essential oil of orange in the presence of phosphoryl chloride.
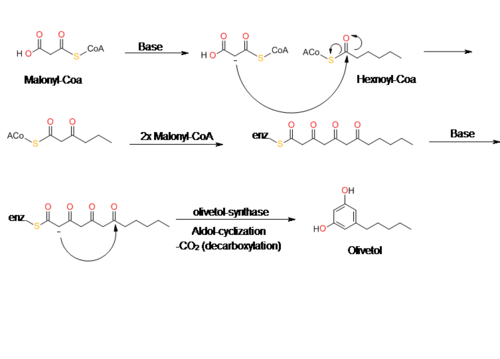
Olivetol is biosynthesized by a polyketide synthase (PKS)-type reaction from hexanoyl-CoA and three molecules of malonyl-CoA by an aldol condensation of a tetraketide intermediate.
In 2009, Taura et al. was able to clone a type III PKS named olivetol synthase (OLS) from Cannabis sativa.
[10] This PKS is a homodimeric protein that consists of a 385 amino acid polypeptide with a molecular mass of 42,585 Da that has high sequence similarity (60-70%) identity to plant PKSs.