Outline of ancient Rome
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Rome: Ancient Rome – former civilization that thrived on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC.
Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to become one of the largest empires in the ancient world.
[1] Political institutions of ancient Rome Roman magistrate Ordinary magistrate Extraordinary magistrate Roman law Military of ancient Rome Military history of ancient Rome Roman era Roman Republic Roman historiography Culture of ancient Rome Ancient Roman architecture Types of buildings and structures Roman art Religion in ancient Rome Roman mythology Latin Languages of the Roman Empire Roman economy





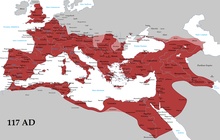
Roman Empire at its greatest extent, in AD 117
vassals





















by Marcus Aurelius



