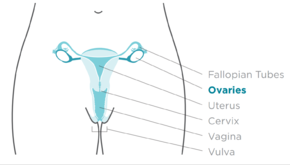
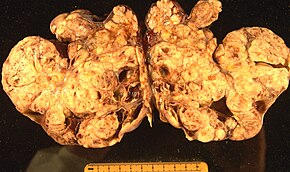
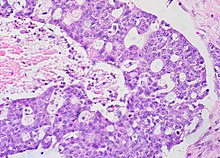
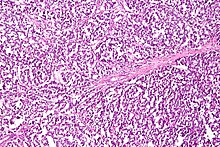
Ovarian cancer
[31] Those who have been treated for infertility but remain nulliparous are at higher risk for epithelial ovarian cancer due to hormonal exposure that may lead to proliferation of cells.
[31] A blood test for a marker molecule called CA-125 is useful in differential diagnosis and in follow up of the disease, but it by itself has not been shown to be an effective method to screen for early-stage ovarian cancer due to its unacceptable low sensitivity and specificity.
[32] Current research is looking at ways to consider tumor marker proteomics in combination with other indicators of disease (i.e. radiology and/or symptoms) to improve diagnostic accuracy.
It provides a consistent framework for interpreting imaging findings, particularly from ultrasound, and assigns risk stratification categories that guide clinical decision-making.
By utilizing a clear set of criteria and terminology, ORADS aims to enhance communication among healthcare providers, increase diagnostic accuracy, and ultimately improve patient outcomes in the evaluation of ovarian and adnexal pathologies.
Additionally, a specialized ORADS calculator is available to facilitate reporting, helping radiologists and clinicians quickly and accurately classify findings according to the system's guidelines.
[78] The development of clots in the legs such as deep vein thromboembolism or in the lungs with pulmonary embolism is reported to be 40% higher in patients with clear-cell carcinoma than other epithelial ovarian cancer subtypes.
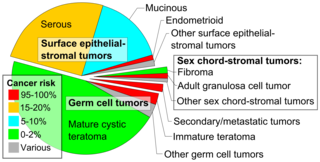
[29] Pseudomyxoma peritonei refers to a collection of encapsulated mucus or gelatinous material in the abdominopelvic cavity, which is very rarely caused by a primary mucinous ovarian tumor.
These tumors produce high levels of estrogen, which causes its characteristic symptoms: menometrorrhagia; endometrial hyperplasia; tender, enlarged breasts; postmenopausal bleeding; and secondary amenorrhea.
Blood tests for alpha-fetoprotein, karyotype, human chorionic gonadotropin, and liver function are used to diagnose germ cell tumor and potential co-occurring gonadal dysgenesis.
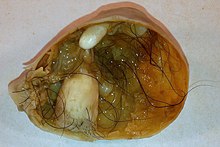
More typically, ovarian squamous cell carcinomas are cervical metastases, areas of differentiation in an endometrioid tumor, or derived from a mature teratoma.
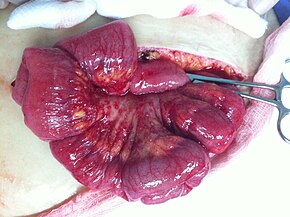
[71] Ovarian cancer is staged using the FIGO staging system and uses information obtained after surgery, which can include a total abdominal hysterectomy via midline laparotomy, removal of (usually) both ovaries and Fallopian tubes, (usually) the omentum, pelvic (peritoneal) washings, assessment of retroperitoneal lymph nodes (including the pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes), appendectomy in suspected mucinous tumors, and pelvic/peritoneal biopsies for cytopathology.
[88] OVCARE — BC Cancer's multi-institutional and multidisciplinary ovarian research group — began recommending salpingectomy at the time of hysterectomy and in place of tubal ligation in 2010.
[19] Women with high risk of ovarian cancer that are currently identified based on family history and genetic testing may benefit from screening.
[29] Screening for CA125, a chemical released by ovarian tumours, with follow-up using ultrasound, was shown to be ineffective in reducing mortality in a large-scale UK study.
[96] Though no definitive studies have been completed, it is shown to be approximately equivalent to primary debulking surgery in terms of survival and shows slightly lower morbidity.
Intraperitoneal chemotherapy can be highly effective because ovarian cancer mainly spreads inside the peritoneal cavity, and higher doses of the drugs can reach the tumors this way.
[31] Germ-cell malignancies are treated differently than other ovarian cancers — a regimen of bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (BEP) is used with 5 days of chemotherapy administered every 3 weeks for 3 to 4 cycles.
[117] Novocure sponsored a phase-2 trial proving efficacy of tumor treating fields in recurrent platinum-resistant ovarian carcinoma, in conjunction with weekly paclitaxel chemotherapy.
[118] Radiotherapy late effects (and occurrence rates) include osteonecrosis (8-20%), bladder ulceration (<3%), vaginal stenosis (>2.5%) and irreversible lumbosacral plexopathy.
However, treatment based only on elevated CA-125 levels and not any symptoms can increase side effects without any prolongation of life, so the implication of the outcome of a CA-125 test can be discussed before taking it.
[29][97] Palliative care can entail treatment of symptoms and complications of the cancer, including pain, nausea, constipation, ascites, bowel obstruction, edema, pleural effusion, and mucositis.
Activities such as traveling, spending additional time with family and friends, ignoring statistics, journaling and increasing involvement in spiritually-based events are adaptive.
It is disproportionately deadly because it lacks any clear early detection or screening test, meaning most cases are not diagnosed until they have reached advanced stages.
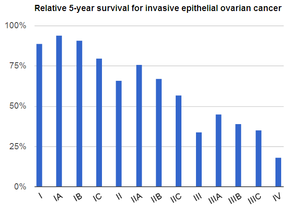
Conversely, negative prognostic factors – those that indicate a worse chance of survival – include rupture of the ovarian capsule during surgery, older age (over 45 years), mucinous type, stage IV, high histologic grade, clear-cell type, upper abdominal involvement, high CA-125 levels, the presence of tumor cells in the blood, and elevated cyclooxygenase-2.
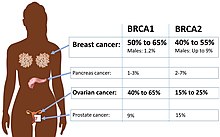
[137] Ashkenazi Jewish women carry mutated BRCA alleles five times more often than the rest of the population, giving them a higher risk developing ovarian cancer.
Germ cell tumors diagnosed during pregnancy are unlikely to have metastasized and can be treated by surgery and, in some cases, chemotherapy, which carries the risk of birth defects.
[121] Researchers from BGI Genomics and Fudan University have uncovered significant findings on ovarian cancer (OV) in Chinese patients, revealing a unique RAD51D variant that may serve as a therapeutic target.
[121] mTOR inhibitors were a highly investigated potential treatment in the 2000s and 2010s, but the side effects of these drugs (particularly hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia) were not well tolerated and the survival benefit not confirmed.
Vintafolide, which consists of an antifolate conjugated with vinblastine, is also in clinical trials; it may prove beneficial because folate receptors are overexpressed in many ovarian cancers.