Propagation delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination, for example in the electromagnetic field, a wire, gas, fluid or solid body.
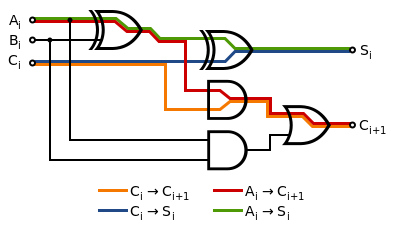
Reducing gate delays allows digital circuits to process data at a faster rate and improve overall performance.
The difference in propagation delays of logic elements is the major contributor to glitches in asynchronous circuits as a result of race conditions.
In computer networks, propagation delay is the amount of time it takes for the head of the signal to travel from the sender to the receiver.
[3][4] This delay is the major obstacle in the development of high-speed computers and is called the interconnect bottleneck in IC systems.