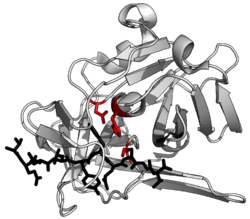
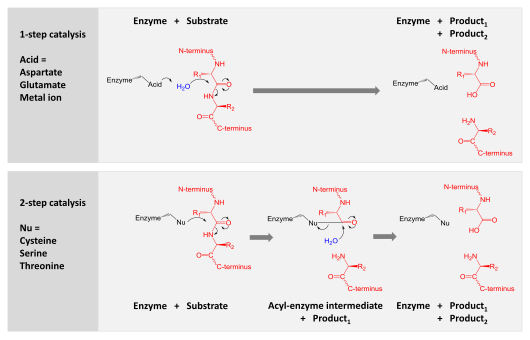
Protease
They have independently evolved multiple times, and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms.
[10] In this database, proteases are classified firstly by 'clan' (superfamily) based on structure, mechanism and catalytic residue order (e.g. the PA clan where P indicates a mixture of nucleophile families).
Catalysis is achieved by one of two mechanisms: Proteolysis can be highly promiscuous such that a wide range of protein substrates are hydrolyzed.
This is the case for digestive enzymes such as trypsin, which have to be able to cleave the array of proteins ingested into smaller peptide fragments.
Blood clotting (such as thrombin) and viral polyprotein processing (such as TEV protease) requires this level of specificity in order to achieve precise cleavage events.
Some snake venoms are also proteases, such as pit viper haemotoxin and interfere with the victim's blood clotting cascade.
Proteases determine the lifetime of other proteins playing important physiological roles like hormones, antibodies, or other enzymes.
By a complex cooperative action, proteases can catalyze cascade reactions, which result in rapid and efficient amplification of an organism's response to a physiological signal.
Bacterial and fungal proteases are particularly important to the global carbon and nitrogen cycles in the recycling of proteins, and such activity tends to be regulated by nutritional signals in these organisms.
[16] The net impact of nutritional regulation of protease activity among the thousands of species present in soil can be observed at the overall microbial community level as proteins are broken down in response to carbon, nitrogen, or sulfur limitation.
[19][20] Archaea use proteases to regulate various cellular processes from cell-signaling, metabolism, secretion and protein quality control.
Protease-containing plant-solutions called vegetarian rennet have been in use for hundreds of years in Europe and the Middle East for making kosher and halal Cheeses.
Vegetarian rennet from Withania coagulans has been in use for thousands of years as a Ayurvedic remedy for digestion and diabetes in the Indian subcontinent.
[28] Natural protease inhibitors include the family of lipocalin proteins, which play a role in cell regulation and differentiation.
Lipophilic ligands, attached to lipocalin proteins, have been found to possess tumor protease inhibiting properties.
Common examples are the trypsin inhibitors found in the seeds of some plants, most notable for humans being soybeans, a major food crop, where they act to discourage predators.