Pseudoautosomal region
[5] The monotremes, including the platypus and echidna, have a multiple sex chromosome system, and consequently have 8 pseudoautosomal regions.
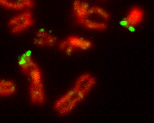
The function of these pseudoautosomal regions is that they allow the X and Y chromosomes to pair and properly segregate during meiosis in males.
[13] Pairing (synapsis) of the X and Y chromosomes and crossing over (recombination) between their pseudoautosomal regions appear to be necessary for the normal progression of male meiosis.
[16] Thus, those cells in which X-Y recombination does not occur will fail to complete meiosis.
Structural and/or genetic dissimilarity (due to hybridization or mutation) between the pseudoautosomal regions of the X and Y chromosomes can disrupt pairing and recombination, and consequently cause male infertility.