Tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene
Tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene (TDAE) is an organic compound with the formula ((CH3)2N)2C=C(N(CH3)2)2, It is a colorless liquid.
The pi-donating tendency of the amine groups strongly enhances the basicity of the molecule, which does exhibit properties of a typical alkene.
[2] TDAE reacts with oxygen in a chemiluminescent reaction to give tetramethylurea.
This returns to the ground state is accompanied by emission of green light with a maximum at 515 nm.
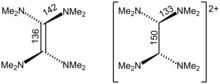
[7] As one of many of examples of its redox behavior forms a charge-transfer salt with buckminsterfullerene:[8] Crystallographic analysis show that TDAE is a highly distorted alkene, the dihedral angle for the two N2C termini is 28°.