Clavulanic acid
[clarification needed] The use of clavulanic acid with penicillins has been associated with an increased incidence of cholestatic jaundice and acute hepatitis during therapy or shortly after.
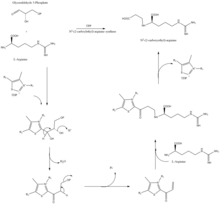
[10] Clavaminate synthase is a non-heme oxygenase dependent on iron and α-keto-glutarate and is encoded by orf5 of the clavulanic acid gene cluster.
[12] β-lactam synthetase is a 54.5 kDa protein that is encoded by orf3 of the clavulanic acid gene cluster, and shows similarity to asparagine synthase – Class B enzymes.
The exact mechanism on how this enzyme works to synthesize the β-lactam is not proven, but is believed to occur in coordination with a CEA synthase and ATP.
[14] Clavulanic acid was discovered around 1974-75 by British scientists working at the drug company Beecham from the bacteria Streptomyces clavuligerus.
However, the similarity in chemical structure allows the molecule to interact with the enzyme β-lactamase secreted by certain bacteria to confer resistance to β-lactam antibiotics.
Clavulanic acid is a suicide inhibitor, covalently bonding to a serine residue in the active site of the β-lactamase.
[1][19][22][20] In animals, including in rodents and/or monkeys, clavulanic acid has shown anxiolytic-like, antidepressant-like, pro-sexual, memory-enhancing, analgesic, antiaddictive, pro-dopaminergic, pro-oxytocinergic, and neuroprotective effects.
[1][20][18][23] The drug has been studied clinically in humans in the treatment of erectile dysfunction,[19] depression,[24][25][26] substance dependence,[27] and pain,[20] with positive or mixed preliminary results for these conditions reported.