Elevation
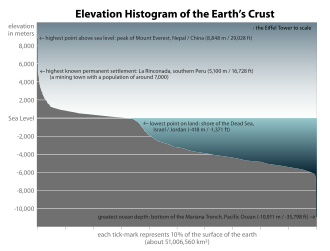
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum).
GIS offers better understanding of patterns and relationships of the landscape at different scales.
Tools inside the GIS allow for manipulation of data for spatial analysis or cartography.
USGS (United States Geologic Survey) is developing a 3D Elevation Program (3DEP) to keep up with growing needs for high quality topographic data.
There are three bare earth DEM layers in 3DEP which are nationally seamless at the resolution of 1/3, 1, and 2 arcseconds.