Verbascoside
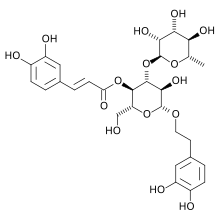
Verbascoside is a polyphenol glycoside[1] in which the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol form an ester and an ether bond respectively, to the rhamnose part of a disaccharide, namely β-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-(4-O-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside.
[2] Verbascoside can be found in species in all the families of the order Lamiales (syn.
In the family Lamiaceae, it can be found in the medicinal plants in the genus Phlomis,[5] in the Scrophulariaceae, in Verbascum phlomoides,[6] Verbascum mallophorum,[7] or, in the family Buddlejaceae, in Buddleja globosa[8] or Buddleja cordata,[9] in the family Bignoniaceae, in Pithecoctenium sp and Tynanthus panurensis, in the family Orobanchaceae, in Cistanche sp and Orobanche rapum-genistae,[2] in the Plantaginaceae, in Plantago lanceolata,[10] in Verbenaceae, in Verbena officinalis (common vervain),[11] Aloysia citrodora (lemon verbena) and Lantana camara,[12] in the Oleaceae, in Olea europaea (olive),[13] in the Lentibulariaceae, in the carnivorous plant Pinguicula lusitanica,[4] and, in the Byblidaceae, in Byblis liniflora.
[16] It can also be produced in hairy roots cultures of Paulownia tomentosa (empress tree, Paulowniaceae).
[7] Although some in vitro genotoxicity of verbascoside has been reported on human lymphocytes with an involvement of PARP-1 and p53 proteins,[18] subsequent in vivo tests reported no genotoxicity for high dosage oral administration.