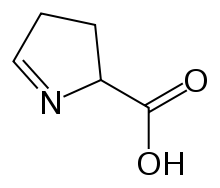
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid
[3] The stereoisomer (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (also referred to as L-P5C) is an intermediate metabolite in the biosynthesis and degradation of proline and arginine.
[4][5][6] In prokaryotic proline biosynthesis, GSA is synthesized from γ-glutamyl phosphate by the enzyme γ-glutamyl phosphate reductase.
In most eukaryotes, GSA is synthesised from the amino acid glutamate by the bifunctional enzyme 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (P5CS).
In many prokaryotes, proline dehydrogenase and P5C dehydrogenase form a bifunctional enzyme that prevents the release of P5C during proline degradation.
[10] This allows an optimum level of proline to be produced from reduced nitrogen to control osmotic stress.