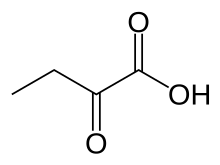
α-Ketobutyric acid
Its conjugate base α-ketobutyrate is the predominant form found in nature (near neutral pH).
α-Ketobutyrate is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, where it is converted to propionyl-CoA by branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex.
This is first through the enzyme mitochondria propionyl-CoA carboxylase with biotin as a cofactor to produce (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA.
Finally, mitochondrial methylmalonyl-CoA mutase with cofactor adenosylcobalamin produces succinyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.
[1] Vin jaune is marked by the formation of sotolon from alpha-ketobutyric acid.