1932 Freeport hurricane
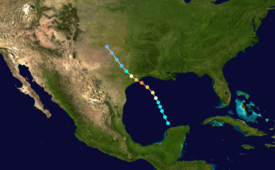
[1] However, it was suggested in later research that the disturbance may have originated from a low-pressure area between Belize and Honduras on August 11.
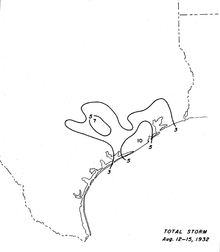
[2] The hurricane proceeded to make landfall early on August 14 just east of Freeport with winds of 150 mph (240 km/h).
[2] In preparation for the storm, 150 vehicles evacuated out of Freeport, while water craft were taken up the Brazos River as far inland as possible.
The 38th division of the Texas National Guard, stationed in Palacios, was alerted due to the oncoming storm.
[6] Occupants in four vehicles were rescued by the United States Coast Guard near San Luis Pass.
[6] Galveston suffered primarily wind damage in the form of unroofed structures and broken windows.
[5] At William P. Hobby Airport in Houston, 11 planes were damaged when a hangar collapsed, resulting in losses of $250,000.
[11] After the storm, the American Red Cross brought supplies to areas affected by the hurricane, requesting as much as $10,000 in relief work.
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown