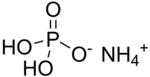
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
[8] Monoammonium phosphate is soluble in water and crystallizes from it as the anhydrous salt in the tetragonal system, as elongated prisms or needles.
[2] Solid monoammonium phosphate can be considered stable in practice for temperatures up to 200 °C, when it decomposes into gaseous ammonia NH3 and molten phosphoric acid H3PO4.
[11] Monoammonium phosphate is industrially prepared by the exothermic reaction of phosphoric acid and ammonia in the correct proportions:[12] Crystalline MAP then precipitates.
Monoammonium phosphate is a widely used crystal in the field of optics due to its birefringence properties.
[8] Being relatively non-toxic[citation needed], MAP is also a popular substance for recreational crystal growing, being sold as toy kits mixed with dyes of various colors.