BRCA2
[16] The human reference BRCA2 gene contains 27 exons, and the cDNA has 10,254 base pairs[17] coding for a protein of 3418 amino acids.
[30] These breaks can be caused by natural and medical radiation or other environmental exposures, but also occur when chromosomes exchange genetic material during a special type of cell division that creates sperm and eggs (meiosis).
By repairing DNA, these proteins play a role in maintaining the stability of the human genome and prevent dangerous gene rearrangements that can lead to hematologic and other cancers.
This condition is caused by extremely reduced levels of the BRCA2 protein in cells, which allows the accumulation of damaged DNA.
Patients with Fanconi anemia are prone to several types of leukemia (a type of blood cell cancer); solid tumors, particularly of the head, neck, skin, and reproductive organs; and bone marrow suppression (reduced blood cell production that leads to anemia).
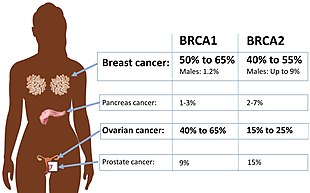
Women having inherited a defective BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have risks for breast and ovarian cancer that are so high and seem so selective that many mutation carriers choose to have prophylactic surgery.
An innate genomic deficit impairs normal responses and exacerbates the susceptibility to disease in organ targets.
[37][38][39][40] The gene was first cloned by scientists at Myriad Genetics, Endo Recherche, Inc., HSC Research & Development Limited Partnership, and the University of Pennsylvania.
[41] Methods to diagnose the likelihood of a patient with mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 getting cancer were covered by patents owned or controlled by Myriad Genetics.
In a large study examining hundreds of cancer and control individuals, this 999del5 mutation was found in 0.6% of the general population.
In the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, loss of the BRCA2 homolog AtBRCA2 causes severe defects in both male meiosis and in the development of the female gametocyte.
It appears that AtBRCA2 acts during meiosis to control the single-strand invasion steps mediated by AtRAD51 and AtDMC1 occurring during meiotic homologous recombinational repair of DNA damages.
[65] Homologs of BRCA2 are also essential for meiosis in the fungus Ustilago maydis,[66] the worm Caenorhabditis elegans,[67][68] and the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster.
[72] BRC repeats conform to a motif consisting of a sequence of about 35 highly conserved amino acids that are present at least once in all BRCA2-like proteins.
The BRCA2 BRC repeats stimulate joint molecule formation by promoting the interaction of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) with DMC1.
[73] Epigenetic alterations in expression of BRCA2 (causing over-expression or under-expression) are very frequent in sporadic cancers (see Table below) while mutations in BRCA2 are rarely found.
In mice and humans, BRCA2 primarily mediates orderly assembly of RAD51 on single-stranded (ss) DNA, the form that is active for homologous pairing and strand invasion.
RAD51 catalyses strand transfer between a broken sequence and its undamaged homologue to allow re-synthesis of the damaged region (see homologous recombination models).
Replication errors past these damages (see translesion synthesis) would lead to increased mutations and cancer.
BRCA2 has been shown to interact with BRCA2 contains a number of 39 amino acid repeats that are critical for binding to RAD51 (a key protein in DNA recombinational repair) and resistance to methyl methanesulphonate treatment.
[116] The BRCA OB1 domain assumes an OB fold, which consists of a highly curved five-stranded beta-sheet that closes on itself to form a beta-barrel.
[116] The BRCA OB3 domain assumes an OB fold, which consists of a highly curved five-stranded beta-sheet that closes on itself to form a beta-barrel.
[116] The Tower domain adopts a secondary structure consisting of a pair of long, antiparallel alpha-helices (the stem) that support a three-helix bundle (3HB) at their end.
The 3HB contains a helix-turn-helix motif and is similar to the DNA binding domains of the bacterial site-specific recombinases, and of eukaryotic Myb and homeodomain transcription factors.
However, the Court also held that manipulation of a gene to create something not found in nature could still be eligible for patent protection.