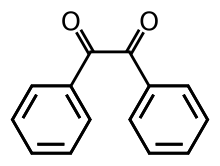
Benzil
[4] The compound's most noteworthy structural feature is the long carbon-carbon bond of 1.54 Å, which indicates the absence of pi-bonding between the two carbonyl centers.
[5] In less hindered analogues (glyoxal, biacetyl, oxalic acid derivatives), the (RCO)2 group adopts a planar, anti-conformation.
It undergoes photobleaching, which allows the curing light to reach deeper layers of the material on longer exposure.
[6] Benzil is a potent inhibitor of human carboxylesterases, enzymes involved in the hydrolysis of carboxylesters and many clinically used drugs.
Benzil is prepared from benzoin, for example with copper(II) acetate:[8] Other suitable oxidizing agents such as nitric acid (HNO3) are used routinely.