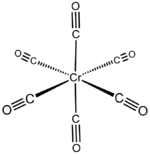
Chromium hexacarbonyl
As described in a 2023 survey of methods "most cost-effective routes for the synthesis of group 6 hexacarbonyls are based on the reduction of the metal chlorides (CrCl3, MoCl5 or WCl6) with magnesium, zinc or aluminium powders... under CO pressures".
[3] Early work on methods included contributions from luminaries such as Walter Hieber, his student Ernst Otto Fischer, and Giulio Natta.
Using specially produced chromium metal will react with CO gas to give Cr(CO)6 directly, although the method is not used commercially.
[4][5][6] On one hand, there has been continuous efforts to calculate the electronic structures (including HOMO and LUMO) as well as its molecular geometry on the chromium hexacarbonyl compound with various approaches.
Alkyl and aryl organolithium reagents (RLi) add to Cr(CO)6 to give anionic acyl complexes.
[17] In reactions, potassium perrhenate (KReO4) is reduced and carbonylated by the chromium reagents and undergoes [C5H5]− ligand-transfer to afford Re(CO)3(C5H5) complex derivatives.