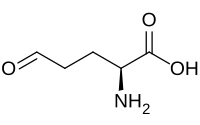
Glutamate-5-semialdehyde
Glutamate-5-semialdehyde is a non-proteinogenic amino acid involved in both the biosynthesis and degradation of proline and arginine (via ornithine),[1][2] as well as in the biosynthesis of antibiotics, such as carbapenems.
It is synthesized by the reduction of glutamyl-5-phosphate by glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase.
Reduction of glutamic acid semialdehyde with sodium borohydride gives hydroxyaminovaleric acid.
[3]