Ribose
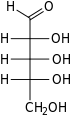
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H.
The naturally occurring form, d-ribose, is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this compound is necessary for coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes.
In its linear form, ribose can be recognised as the pentose sugar with all of its hydroxyl functional groups on the same side in its Fischer projection.
[15][16] Ribose is an aldopentose (a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms that, in its open chain form, has an aldehyde functional group at one end).
The deoxyribose derivative found in DNA differs from ribose by having a hydrogen atom in place of the hydroxyl group at C2'.
The "d-" in the name d-ribose refers to the stereochemistry of the chiral carbon atom farthest away from the aldehyde group (C4').
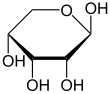
In d-ribose, as in all d-sugars, this carbon atom has the same configuration as in d-glyceraldehyde.Relative abundance of forms of ribose in solution: β-d-ribopyranose (59%), α-d-ribopyranose (20%), β-d-ribofuranose (13%), α-d-ribofuranose (7%) and open chain (0.1%).
[18] This puckering is achieved by displacing an atom from the plane, relieving the strain and yielding a more stable conformation.
Ribose is a building block in secondary signaling molecules such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) which is derived from ATP.
cAMP, a secondary messenger, then goes on to activate protein kinase A, which is an enzyme that regulates cell metabolism.
Protein kinase A regulates metabolic enzymes by phosphorylation which causes a change in the cell depending on the original signal molecule.
In de novo, amino acids, carbon dioxide, folate derivatives, and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) are used to synthesize nucleotides.
By adding an O-alkyl group, the nuclear resistance of the RNA is increased because of additional stabilizing forces.
[28] Along with phosphorylation, ribofuranose molecules can exchange their oxygen with selenium and sulfur to produce similar sugars that only vary at the 4' position.
Increased lipophilicity makes these species more suitable for use in techniques such as PCR, RNA aptamer post-modification, antisense technology, and for phasing X-ray crystallographic data.
Essentially, administering supplemental d-ribose bypasses an enzymatic step in the pentose phosphate pathway by providing an alternate source of 5-phospho-d-ribose 1-pyrophosphate for ATP production.
Supplemental d-ribose enhances recovery of ATP levels while also reducing cellular injury in humans and other animals.
One study suggested that the use of supplemental d-ribose reduces the instance of angina in men with diagnosed coronary artery disease.
[31] d-Ribose has been used to treat many pathological conditions, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, and myocardial dysfunction.