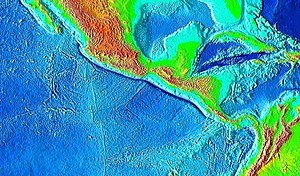
Middle America Trench
The Middle America Trench is a major subduction zone, an oceanic trench in the eastern Pacific Ocean off the southwestern coast of Middle America, stretching from central Mexico to Costa Rica.
The trench is 1,700 miles (2,750 km) long and is 21,880 feet (6,669 m) at its deepest point.
Many large earthquakes have occurred in the area of the Middle America Trench.
[1] The Middle America Trench can be divided into a northern and a southern section.
[2] On the landward side, the division is demarcated along the Polochic-Motagua fault system (see Motagua Fault), the boundary between the North American plate and the Caribbean plate.