Percentile
Percentiles are expressed in the same unit of measurement as the input scores, not in percent; for example, if the scores refer to human weight, the corresponding percentiles will be expressed in kilograms or pounds.
In the limit of an infinite sample size, the percentile approximates the percentile function, the inverse of the cumulative distribution function.
Percentiles are a type of quantiles, obtained adopting a subdivision into 100 groups.
A related quantity is the percentile rank of a score, expressed in percent, which represents the fraction of scores in its distribution that are less than it, an exclusive definition.
For percentile ranks, a score is given and a percentage is computed.
In contrast, for percentiles a percentage is given and a corresponding score is determined, which can be either exclusive or inclusive.
There is no standard definition of percentile;[1][2][3] however, all definitions yield similar results when the number of observations is very large and the probability distribution is continuous.
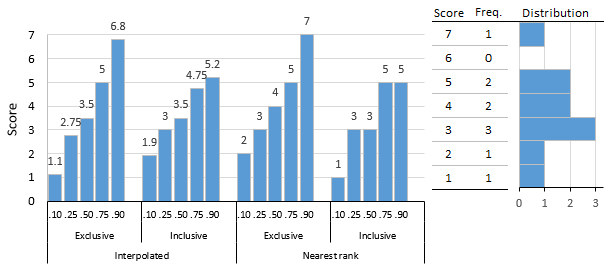
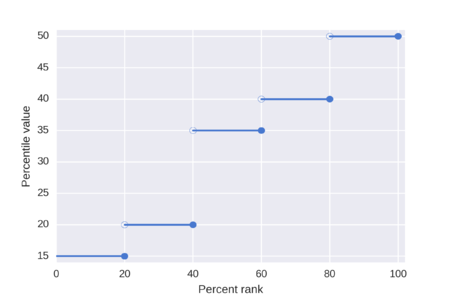
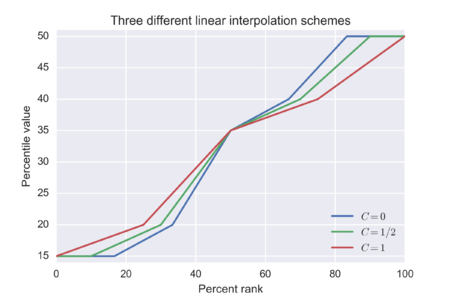
[4] In the limit, as the sample size approaches infinity, the 100pth percentile (0 The normal distribution is plotted along an axis scaled to standard deviations, or sigma ( Note, however, that only a very small proportion of individuals in a population will fall outside the −3σ to +3σ range. Percentiles represent the area under the normal curve, increasing from left to right. Note that in theory the 0th percentile falls at negative infinity and the 100th percentile at positive infinity, although in many practical applications, such as test results, natural lower and/or upper limits are enforced. When ISPs bill "burstable" internet bandwidth, the 95th or 98th percentile usually cuts off the top 5% or 2% of bandwidth peaks in each month, and then bills at the nearest rate. The reason this statistic is so useful in measuring data throughput is that it gives a very accurate picture of the cost of the bandwidth. Physicians will often use infant and children's weight and height to assess their growth in comparison to national averages and percentiles which are found in growth charts. The 85th percentile speed of traffic on a road is often used as a guideline in setting speed limits and assessing whether such a limit is too high or low. Hyndman and Fan [1] identified nine and most statistical and spreadsheet software use one of the methods they describe. The figure shows a 10-score distribution, illustrates the percentile scores that result from these different algorithms, and serves as an introduction to the examples given subsequently. Algorithms used by statistical programs typically use interpolation methods, for example, the percentile.exc and percentile.inc functions in Microsoft Excel. The Interpolated Methods table shows the computational steps. Given the order statistics we seek a linear interpolation function that passes through the points uses the floor function to represent the integral part of positive x, whereas uses the mod function to represent its fractional part (the remainder after division by 1). As we can see, x is the continuous version of the subscript i, linearly interpolating v between adjacent nodes. , and a constant that is a function of the sample size N: There is the additional requirement that the midpoint of the range , which may mean the absence of a one-to-one correspondence in the wider region. (Sources: Matlab "prctile" function,[9][10]) where Furthermore, let The inverse relationship is restricted to a narrower region: [Source: Some software packages, including NumPy[11] and Microsoft Excel[3] (up to and including version 2013 by means of the PERCENTILE.INC function). , the only one of the three variants with this property; hence the "INC" suffix, for inclusive, on the Excel function. However, as the "EXC" suffix indicates, the Excel version excludes both endpoints of the range of p, i.e., The inverse is restricted to a narrower region: In addition to the percentile function, there is also a weighted percentile, where the percentage in the total weight is counted instead of the total number.