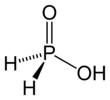
Hypophosphorous acid
[4] The acid is prepared industrially via a two step process: Firstly, elemental white phosphorus reacts with alkali and alkaline earth hydroxides to give an aqueous solution of hypophosphites: Any phosphites produced in this step can be selectively precipitated out by treatment with calcium salts.
Pure anhydrous hypophosphorous acid can be formed by the continuous extraction of aqueous solutions with diethyl ether.
[6] HPA is usually supplied as a 50% aqueous solution and heating at low temperatures (up to about 90 °C) prompts it to react with water to form phosphorous acid and hydrogen gas.
Owing to its ability to function as a mild reducing agent and oxygen scavenger it is sometimes used as an additive in Fischer esterification reactions, where it prevents the formation of colored impurities.
It is effective for various transition metals ions (i.e. those of: Co, Cu, Ag, Mn, Pt) but is most commonly used to reduce nickel.