Polar circle
Due to their inherent climate environment, the bulk of the Arctic Circle, much of which is sea, is sparsely settled whereas this applies to all of Antarctica which is mainly land and sheltered ice shelves.
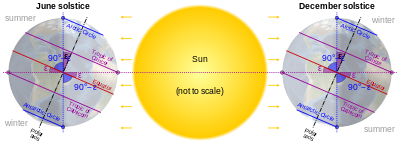
Instead, atmospheric refraction and the Sun's light reaching the planet as an extended object rather than a point source means that just within each circle the Earth's surface does not experience any proper polar night, 24 hours where the sun does not rise.
The axial tilt also exhibits long-term variations as described in the reference article (a difference of 1 second of arc (″) in the tilt is equivalent to a change of about 31 metres north or south in the positions of the polar circles on the Earth's surface).
[citation needed] A further global factor for this numerical range is Earth's nutation, which is a very small change in tilt.
Observers higher above sea level can see a tiny amount of the Sun's disc (see horizon) where at lower places it would not rise.