Lipid-based nanoparticle
A novel squaramide lipid (a partially aromatic four-membered ring that can participate in pi–pi interactions) has been used as part of the delivery system used, for example, by Moderna.
Biological membrane lipids, such as phospholipids, sphingomyelins, bile salts (sodium taurocholate), and sterols (cholesterol) are used as stabilizers.
Obtaining size distributions in the range of 30-180 nm is possible using ultrasonication at the cost of long sonication time.
Solvent-emulsification is suitable in preparing small, homogeneously sized lipid nanoparticles dispersions with the advantage of avoiding heat.
However, various measures to monitor and evaluate product quality are integrated in every step of LNP manufacturing and include testing of polydispersity, particle size, drug loading efficiency and endotoxin levels.
[citation needed] The conventional approaches such as use of permeation enhancers, surface modification, prodrug synthesis, complex formation and colloidal lipid carrier-based strategies have been developed for the delivery of drugs to intestinal lymphatics.
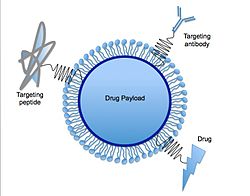
[10] Various functions such as molecules for targeting, PEG chains for stealth properties,[18] or thiol groups for adhesion via disulfide bond formation[19] can be immobilized on their surface.
[24] Advantages of SLNs include the use of physiological lipids (which decreases the danger of acute and chronic toxicity), the avoidance of organic solvents, a potential wide application spectrum (dermal, per os, intravenous) and the high pressure homogenization as an established production method.
[29] During the late 1990s and 2000s, Pieter Cullis, while at the University of British Columbia, developed ionizable cationic lipids which are "positively charged at an acidic pH but neutral in the blood.
"[6] Cullis also led the development of a technique involving careful adjustments to pH during the process of mixing ingredients in order to create LNPs which could safely pass through the cell membranes of living organisms.
[26][30] As of 2021, the current understanding of LNPs formulated with such ionizable cationic lipids is that they enter cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis and end up inside endosomes.
[6] Elucidation of intestinal lymphatic absorption mechanism from solid lipid nanoparticles using Caco-2 cell line as in vitro model was developed.
[32] Several researchers have shown the enhancement of oral bioavailibility of poorly water-soluble drugs when encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticle.
To elucidate the absorption mechanism, from solid lipid nanoparticle, human excised Caco-2 cell monolayer could be alternative tissue for development of an in-vitro model to be used as a screening tool before animal studies are undertaken.