South America
[j] The ABC islands (Dutch Caribbean) and Trinidad and Tobago are geologically located on the South-American continental shelf,[8][9] and thus may be considered part of South America as well.
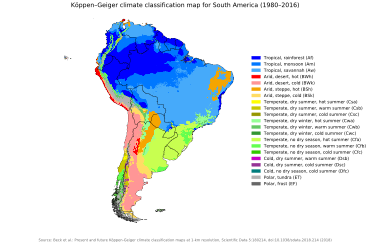
The geography of western South America is dominated by the Andes mountains; in contrast, the eastern part contains both highland regions and vast lowlands where rivers such as the Amazon, Orinoco and Paraná flow.
Relative to Africa, Asia, and Europe, post-1900 South America has been a peaceful continent with few wars,[11][12][k] although high rates of violent crime remain a concern in some countries.
The fluctuation in the price of commodities in international markets has led historically to major highs and lows, booms and busts, in the economies of South American states, often causing political instability.
), the State of Nueva Esparta, and the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela sit on the northern portion of the South American continental shelf and are sometimes considered parts of the continent.
It is home to many unique species of animals including the llama, anaconda, piranha, jaguar, vicuña, and tapir, and to one of the largest known insects in the world, the Titan beetle.
[46] The rise of plant growing and the subsequent appearance of permanent human settlements allowed for the multiple and overlapping beginnings of civilizations in South America.
Other important Pre-Columbian cultures include: the Cañaris (in south central Ecuador), Chimú Empire (1300–1470, Peruvian northern coast), Chachapoyas, and the Aymaran kingdoms (1000–1450, Western Bolivia and southern Peru).
Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers; this included many gold and silver sculptures and other artifacts found in South America, which were melted down before their transport to Spain or Portugal.
Spaniards and Portuguese brought the western European architectural style to the continent, and helped to improve infrastructures like bridges, roads, and the sewer system of the cities they discovered or conquered.
European colonists were heavily dependent on indigenous labor during the initial phases of settlement to maintain the subsistence economy, and natives were often captured by expeditions.
Despite the Portuguese loyalties of garrisons in Bahia, Cisplatina and Pará, independence was diplomatically accepted by Portugal in 1825, on condition of a high compensation paid by Brazil mediated by the United Kingdom.
[59] In 1825, the proclamation of independence of Cisplatina led to the Cisplatine War between historical rivals the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, Argentina's predecessor.
In 1851, the Brazilian Empire, supporting the centralizing unitarians, and the Uruguayan government invaded Argentina and deposed the caudillo, Juan Manuel Rosas, who ruled the confederation with an iron hand.
Early in the 20th century, the three wealthiest South American countries engaged in a vastly expensive naval arms race which began after the introduction of a new warship type, the "dreadnought".
[72] Colombia has had an ongoing, though diminished internal conflict, which started in 1964 with the creation of Marxist guerrillas (FARC-EP) and then involved several illegal armed groups of leftist-leaning ideology as well as the private armies of powerful drug lords.
[73] Nonetheless, allegations of corruption are still very common, and several countries have developed crises which have forced the resignation of their governments, although, on most occasions, regular civilian succession has continued.
International indebtedness became a significant problem in the late 1980s, and some countries, despite having strong democracies, have not developed political institutions capable of handling such crises without resorting to unorthodox economic policies.
It is currently the only inhabited continent in the world without monarchies; the Empire of Brazil existed during the 19th century and there was an unsuccessful attempt to establish a Kingdom of Araucanía and Patagonia in southern Argentina and Chile.
[78] This new political organization, known as Union of South American Nations, seeks to establish free movement of people, economic development, a common defense policy and the elimination of tariffs.
South America has shown good signs of economic stability, with controlled inflation and exchange rates, continuous growth, a decrease in social inequality and unemployment – factors that favor industry.
Accounting for 29 percent of GDP, Brazil's industries range from automobiles, steel, and petrochemicals to computers, aircraft (Embraer), food, pharmaceutical, footwear, metallurgy and consumer durables.
[187][188] Historic relics, architectural and natural wonders, a diverse range of foods and culture, colorful cities, and pretty landscapes attract millions of tourists every year to South America.
Some of the most visited places in the region are Rio de Janeiro, Florianópolis, Iguazu Falls, São Paulo, Armação dos Búzios, Salvador, Bombinhas, Angra dos Reis, Balneário Camboriú, Paraty, Ipojuca, Natal, Cairu, Fortaleza and Itapema in Brazil;[189] Buenos Aires, Bariloche, Salta, Jujuy, Perito Moreno Glacier, Valdes Peninsula, Guarani Jesuit Missions in the cities of Misiones and Corrientes, Ischigualasto Provincial Park, Ushuaia and Patagonia in Argentina;[190] Isla Margarita, Angel Falls, Los Roques archipelago, Gran Sabana in Venezuela; Machu Picchu, Lima, Nazca Lines, Cuzco in Peru; Lake Titicaca, Salar de Uyuni, La Paz, Jesuit Missions of Chiquitos in Bolivia; Tayrona National Natural Park, Santa Marta, Bogotá, Cali, Medellín, Cartagena in Colombia, and the Galápagos Islands in Ecuador.
In the central and western regions of Bolivia, Andean and folklore music like Diablada, Caporales and Morenada are the most representative of the country, which were originated by European, Aymara and Quechua influences.
The literature of South America has attracted considerable critical and popular acclaim, especially with the Latin American Boom of the 1960s and 1970s, and the rise of authors such as Mario Vargas Llosa, Gabriel García Márquez in novels and Jorge Luis Borges and Pablo Neruda in other genres.
The artist Oswaldo Guayasamín (1919–1999) from Ecuador, represented with his painting style the feeling of the peoples of Latin America[193] highlighting social injustices in various parts of the world.
Other sports include basketball, cycling, polo, volleyball, futsal, motorsports, rugby (mostly in Argentina and Uruguay), handball, tennis, golf, field hockey, boxing, and cricket.
The Brazilian Highlands have a much higher hydroelectric potential than the Andean region[citation needed] and its possibilities of exploitation are greater due to the existence of several large rivers with high margins and the occurrence of great differences forming huge cataracts, such as those of Paulo Afonso, Iguaçu and others.
Brazil has 44 international airports, such as those in Rio de Janeiro, Brasília, Belo Horizonte, Porto Alegre, Florianópolis, Cuiabá, Salvador, Recife, Fortaleza, Belém and Manaus, among others.