Synthetic drug
Phenethylamine can relieve depressive symptoms while Alprazolam can treat insomnia, panic attack and anxiety.
[3] The adverse effects of synthetic drugs are hard to determine as they usually contain other chemicals with variable concentrations and human studies are limited.
Synthetic cannabinoids can cause cardiovascular problems such as tachyarrhythmia, seizures, psychological disorders and potential carcinogenic effects.
[6] Synthetic cannabinoids are best avoided in users who suffer from rapid heart rate, vomiting, agitation, confusion and hallucination.
In addition, use of phenethylamine might cause people with bipolar disorder to convert from depression to mania and worsened schizophrenia symptoms.
Stimulants can modulate the levels and action of monoamine neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline for vasoconstriction and elevation in blood pressure.
In some animal studies, Phenethylamines have negative inotropism in isolated cardiac tissues of rats due to stimulation of TAAR1, which is in contrast with human pharmacology.
[12] Alprazolam binds to GABA type-A benzodiazepine receptor sites which are the members of the pentameric ligand-gated ion channel (PLGIC) superfamily.
Once attached, conformational changes occur which stabilize the receptors and inhibitory signals are produced[13] Synthetic cannabinoids are delivered by smoking.
The first possible pathway is metabolism by MAO-B (an intracellular enzyme mainly in the brain and tightly bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria which deaminates free primary and secondary amines) to form phenylacetic acid due to MAO-B selectivity on non-polar aromatic amines.
Then, the metabolites undergo N-methylation by non-specific N-methyltransferase(NMT) or by phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase (PNMT) (found in the adrenal medulla) to form secondary amines and sympathetic neurotransmitter noradrenaline.
The second possible pathway is deamination of the drug by the semi-carbazide-sensitive amine oxidases (SSAO) (found in the vascular tissue and have similar metabolism to MAO).
[14] Alprazolam has high oral bioavailability (84-91%) in which its maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is reached after 1 to 2 hours.
If the drug is structurally modified, the original antibodies will respond in a different fashion which will give false positive or negative results.
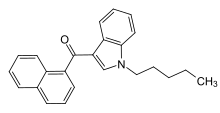
CB1 in particular, is expressed in the central nervous system and largely responsible for the psychoactive effect..[16] A typical agonist consists of the following components: head, linker core and tail.
The aromatic rings from the aminoalkylindole class also play the role of enhancing the affinity by forming a hydrophobic cavity to stabilize the CB1 receptors.
[17] As legislation becomes tightened under the monitoring of Early Warning System (EWS), attempts are made to alter the structure which produce new analogues such as the Cyclopropylindoles (UR-144) and adamantylindoles (APINACA).
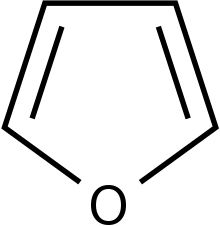
Furthermore, attachment of an electron withdrawing groups and heterocyclic rings such as thiophene and furan will increase the inhibitory effect against bacteria.
When a methyl group is attached at the alpha position, the compound becomes amphetamines which has the ability to modulate the 5HT-2A serotonin receptors.
Established in 1997, It formed part of the framework that allows the European Union to rapidly detect NPS that pose a risk to the public's health.
It is based on the premise of modifying the structure of illicit drugs to evade international control measures.
Seizures reports from police and customs authorities have shown that new benzodiazepine is not of great interest compared to other NPS groups.