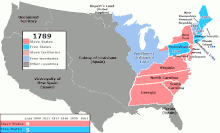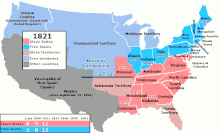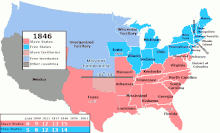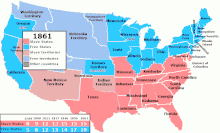
United States labor law
In 2020, the Supreme Court of the United States ruled in Bostock v. Clayton County that discrimination solely on the grounds of sexual orientation or gender identity violates Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
[44] But despite the Democratic Party's overwhelming electoral victory, the Supreme Court continued to strike down legislation, particularly the National Industrial Recovery Act of 1933, which regulated enterprise in an attempt to ensure fair wages and prevent unfair competition.
A series of Supreme Court decisions, held the National Labor Relations Act of 1935 not only created minimum standards, but stopped or "preempted" states enabling better union rights, even though there was no such provision in the statute.
The last major labor law statute, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 created rights to well regulated occupational pensions, although only where an employer had already promised to provide one: this usually depended on collective bargaining by unions.
Alongside the purpose of labor legislation to mitigate inequality of bargaining power and redress the economic reality of a worker's position, the multiple factors found in the Restatement of Agency must be considered, though none is necessarily decisive.
627, International Union of Operating Engineers, AFL-CIO,[80] the Supreme Court found that the DC Circuit had legitimately identified two corporations as a single employer given that they had a "very substantial qualitative degree of centralized control of labor",[81] but that further determination of the relevant bargaining unit should have been remitted to the NLRB.
In West Coast Hotel Co. v. Parrish Hughes CJ held (over four dissenters still arguing for Freedom of Contract) that a Washington law setting minimum wages for women was constitutional because the state legislatures should be enabled to adopt legislation in the public interest.
In Lockheed Corp. v. Spink a majority of seven judges held that an employer could alter a plan, to deprive a 61-year-old man of full benefits when he was reemployed, unbound by fiduciary duties to preserve what an employee had originally been promised.
[196] For example, in Donovan v. Bierwirth, the Second Circuit held that trustees of a pension which owned shares in the employees' company as a takeover bid was launched, because they faced a potential conflict of interest, had to get independent legal advice on how to vote, or possibly abstain.
[217] The American model developed from the Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914,[218] which declared the "labor of a human being is not a commodity or article of commerce" and aimed to take workplace relations out of the reach of courts hostile to collective bargaining.
Using the Sherman Act of 1890, which was intended to break up business cartels, the Supreme Court imposed an injunction on striking workers of the Pullman Company, and imprisoned the leader, and future presidential candidate, Eugene Debs.
In Adair v. United States,[251] and Coppage v. Kansas,[252] the Supreme Court, over powerful dissents,[253] asserted the Constitution empowered employers to require employees to sign contracts promising they would not join a union.
[273] However, in NLRB v. Sands Manufacturing Co. the Supreme Court held an employer did not commit an unfair trade practice by shutting down a water heater plant, while the union was attempting to prevent new employees being paid less.
[279] For example, in United Steelworkers v. Warrior & Gulf Navigation Co a group of employees at a steel transportation works in Chickasaw, Alabama, requested the corporation go to arbitration over layoffs and outsourcing of 19 staff on lower pay to do the same jobs.
[283] But then, in 2009 in 14 Penn Plaza LLC v. Pyett Thomas J announced with four other judges that apparently "[n]othing in the law suggests a distinction between the status of arbitration agreements signed by an individual employee and those agreed to by a union representative.
[290] For example, in one of the first cases, NLRB v. Jones & Laughlin Steel Corp, the US Supreme Court held that the National Labor Relations Board was entitled to order workers be rehired after they had been dismissed for organizing a union at their plant in Aliquippa, Pennsylvania.
[299] Also, in Lechmere, Inc. v. National Labor Relations Board the Supreme Court held 6 to 3 that an employer was entitled to prevent union members, who were not employees, from entering the company parking lot to hand out leaflets.
For example, in Pattern Makers League of North America v. NLRB an employer claimed a union had committed an unfair practice by attempting to enforce fines against employees who had been members, but quit during a strike when their membership agreement promised they would not.
[117] The first major case, Garner v. Teamsters Local 776, decided a Pennsylvania statute was preempted from providing superior remedies or processing claims quicker than the NLRB because "the Board was vested with power to entertain petitioners' grievance, to issue its own complaint" and apparent "Congress evidently considered that centralized administration of specially designed procedures was necessary to obtain uniform application of its substantive rules".
[309] Most recently in Chamber of Commerce v. Brown seven judges on the Supreme Court held that California was preempted from passing a law prohibiting any recipient of state funds either from using money to promote or deter union organizing efforts.
The National Labor Relations Act of 1935 only covers "employees" in the private sector, and a variety of state laws attempt to suppress government workers' right to strike, including for teachers,[325] police and firefighters, without adequate alternatives to set fair wages.
[381] After state laws experimented, President Franklin D. Roosevelt's Executive Order 8802 in 1941 set up the Fair Employment Practice Committee to ban discrimination by "race, creed, color or national origin" in the defense industry.
[412] Disparate treatment can be justified under CRA 1964 §2000e-2(e) if an employer shows selecting someone reflects by "religion, sex, or national origin is a bona fide occupational qualification reasonably necessary to the normal operation of that particular business or enterprise.
[423] Furthermore, in Robinson v. Shell Oil Co. the Supreme Court held that writing a negative job reference, after a plaintiff brought a race discrimination claim, was unlawful retaliation: employees were protected even if they had been fired.
[430] In a further concurrence, Scalia J said "resolution of this dispute merely postpones the evil day" when a disparate impact might be found unconstitutional, against the [[Equal Protection Clause]] because, in his view, the lack of a good faith defense meant employers were compelled to do "racial decision making" that "is ...
[439] Nevertheless, the majority held that the gender pay provisions could be worse because, for example, an employer could apply ""a bona fide job rating system," so long as it does not discriminate on the basis of sex", whereas the same would not be possible for other claims under the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
[461] In the late 19th century, employment at will was popularized by academic writers as an inflexible legal presumption,[462] and state courts began to adopt it, even though many had presumed that contract termination usually required notice and justifications.
This was not made out in the leading case, Howard Johnson Co. v. Detroit Local Joint Executive Board, where the new owner of a restaurant and motor lodge business retained 9 out of 53 former employees, but hired 45 new staff of its own.
It was long acknowledged that the law should ensure nobody is denied a job by unreasonable restrictions by the state or private parties, and the Supreme Court said in Truax v. Raich that "the right to work for a living in the common occupations of the community is of the very essence of the personal freedom and opportunity".
[504] During the New Deal with unemployment having reached 20% after the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the Emergency Relief Appropriation Act of 1935 empowered the President to create the Works Progress Administration, which aimed to directly employ people on fair wages.