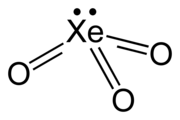
Xenon trioxide
It is a very powerful oxidizing agent, and liberates oxygen from water slowly, accelerated by exposure to sunlight.
[3] Above 25 °C, xenon trioxide is very prone to violent explosion: When it dissolves in water, an acidic solution of xenic acid is formed: This solution is stable at room temperature and lacks the explosive properties of xenon trioxide.
It oxidises carboxylic acids quantitatively to carbon dioxide and water.
[5] These are not stable and begin to disproportionate into perxenates (+8 oxidation state) and xenon and oxygen gas.
[6] Solid perxenates containing XeO4−6 have been isolated by reacting XeO3 with an aqueous solution of hydroxides.