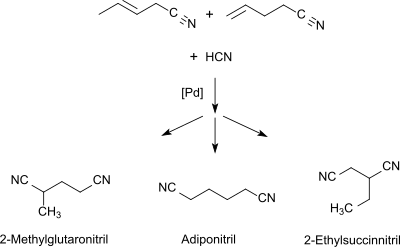
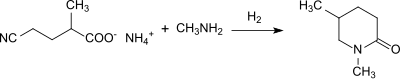2-Methylglutaronitrile
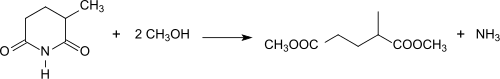
It is the starting compound for the vitamin nicotinamide and for the diester dimethyl-2-methylglutarate and the ester amide methyl 5-(dimethylamino)-2-methyl-5-oxopentanoate, which are promoted as green solvents.
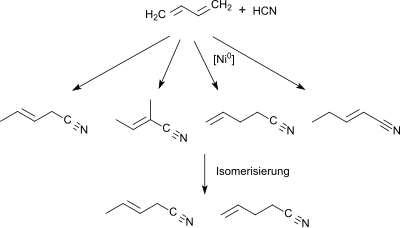
Starting from 1,3-butadiene or a butadiene-rich C4-section (> 40% by volume) from a naphtha steamcracker in the first stage a mixture of pentenenitriles is obtained through hydrocyanation (using as catalyst Ni0-phosphine [PR3][2] or phosphite or phosphonite [P(OR)2R][3]).
[17] Starting from 2-methylglutaronitrile the hydrolysis to 2-methylglutaric acid can also be accomplished via the 2-methylglutarimide obtained by heating a 2-methylglutaronitrile/water mixture to 275 °C in the presence of a titanium dioxide catalyst in yields of 94%.
[21] The diester can be selectively converted into a mixture of 1- or 5-substituted methyl ester amides with dimethylamine in methanol/sodium methoxide,[22] which is used under the name Rhodiasolv Polarclean as formulation auxiliaries for crop protection preparations.
[6] The resulting ester amides are readily biodegradable and good solvents for a variety of different plant protection agents (such as insecticides or fungicides), also compared to the frequently used N-methylpyrrolidone, cyclohexanone or isophorone.
Other esteramides are derived, e. g. from 2-methylglutaronitrile which, after alkaline hydrolysis, is converted into 2-methylglutaric acid, cyclized with acetic anhydride to give 2-methylglutaric anhydride, reacted with dimethylamine to form the monoamide, reacted to an acid chloride with thionyl chloride and formed to an ester with more hydrophobic alcohols (like butanols or cyclohexanol).