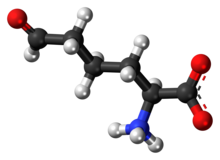
Allysine
Allysine is a derivative of lysine that features a formyl group in place of the terminal amine.
It is produced by aerobic oxidation of lysine residues by the enzyme lysyl oxidase.
[2] Increased allysine concentration in tissues has been correlated to the presence of fibrosis.
[3] Allysine residues react with sodium 2-naphthol-6-sulfonate to produce a fluorescent bis-naphtol-allysine product.
[4] In another assay, allysine-containing proteins are reduced with sodium borohydride to give a peptide containing the 6-hydroxynorleucine (6-hydroxy-2-aminocaproic acid) residue, which (unlike allysine) is stable to proteolysis.