Alpha elimination
The definition of alpha elimination differs for organometallic and organic chemistry.
Alpha eliminations contrasts with beta eliminations, which are commonly used to generate alkenes: Both alpha- and beta-eliminations typically require strong base.
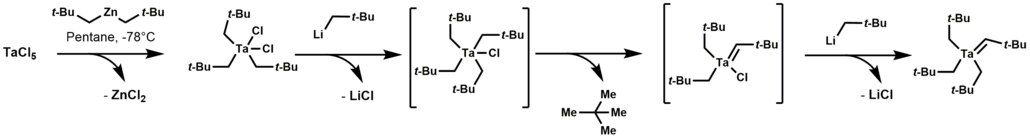
In organometallic chemistry, alpha elimination refers to reactions of this type (other spectator ligands omitted):[2] Well studied case are found in organotantalum chemistry leading to an alkylidene derivatives.
Specifically, tetraalkyl-monochloro-tantalum complex undergoes α-hydrogen elimination, followed by alkylation of the remaining chloride to give a derivative with a Ta=C bond.
[3] Alpha elimination contrasts with β-hydride elimination, whereby an alkyl group bonded to a metal centre is converted into the corresponding metal-bonded hydride and an alkene.