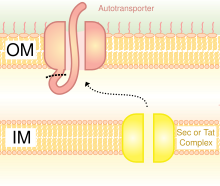
Bacterial display
Libraries of polypeptides displayed on the surface of bacteria can be screened using flow cytometry or iterative selection procedures (biopanning).
Bacterial display can be used to find target proteins with desired properties and can be used to make affinity ligands which are cell-specific.
This system can be used in many applications including the creation of novel vaccines, the identification of enzyme substrates and finding the affinity of a ligand for its target protein.
Then, they explored the versatility of the permissive sites (size limit, nature of the epitope,...) that were all located in surface-exposed loops of the trimeric outer membrane porin, aiming at developing multivalent live bacterial vaccines (12-15).
Information on the size of the cell can be obtained by the scattering of light and if binding of the heterologous protein with the target protein/cell has occurred, there will be more fluorescence emitted.
This method is usually combined with FACS, and the addition of a non-fluorescent target protein competitor is beneficial to obtaining more accurate binding affinities.
Adding a competitor reduces the chance of target proteins rebinding, which would render the binding affinity less accurate.
[8] By DNA randomization millions of cyclic peptides displayed on cell surface can be screened against a protein target using high-throughput FACS.
Displayed proteins are fluorescently tagged with GFP, so binding interactions between peptides and target cells can be seen by flow cytometry.
Control samples are required in order to measure fluorescence levels in the absence of displayed peptides.
Under similar conditions, selection of bacterial-displayed peptides to model protein streptavidin proved worse.
Charbit A, Boulain JC, Ryter A, Hofnung M. Probing the topology of a bacterial membrane protein by genetic insertion of a foreign epitope; expression at the cell surface.
Charbit A, Sobczak E, Michel ML, Molla A, Tiollais P, Hofnung M. Presentation of two epitopes of the preS2 region of hepatitis B virus on live recombinant bacteria.
Charbit A, Molla A, Saurin W, Hofnung M.Versatility of a vector for expressing foreign polypeptides at the surface of gram-negative bacteria.
Newton SM, Klebba PE, Michel V, Hofnung M, Charbit A. Topology of the membrane protein LamB by epitope tagging and a comparison with the X-ray model.