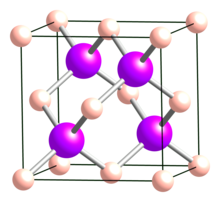
Boron arsenide
BAs is a cubic (sphalerite) semiconductor in the III-V family with a lattice constant of 0.4777 nm and an indirect band gap of 1.82 eV.
[9] In 2023, a study in journal Nature reported that subjected to high pressure BAs decrease its thermal conductivity contrary to the typical increase seen in most materials.
Experimental integration with gallium nitride transistors to form GaN-BAs heterostructures has been demonstrated and shows better performance than the best GaN HEMT devices on silicon carbide or diamond substrates.
[16] First-principles calculations have predicted that the thermal conductivity of cubic BAs is remarkably high, over 2,200 W/(m·K) at room temperature, which is comparable to that of diamond and graphite.
[20] Later, defect-free boron arsenide crystals have been experimentally realized and measured with an ultrahigh thermal conductivity of 1300 W/(m·K), consistent with theory predictions.